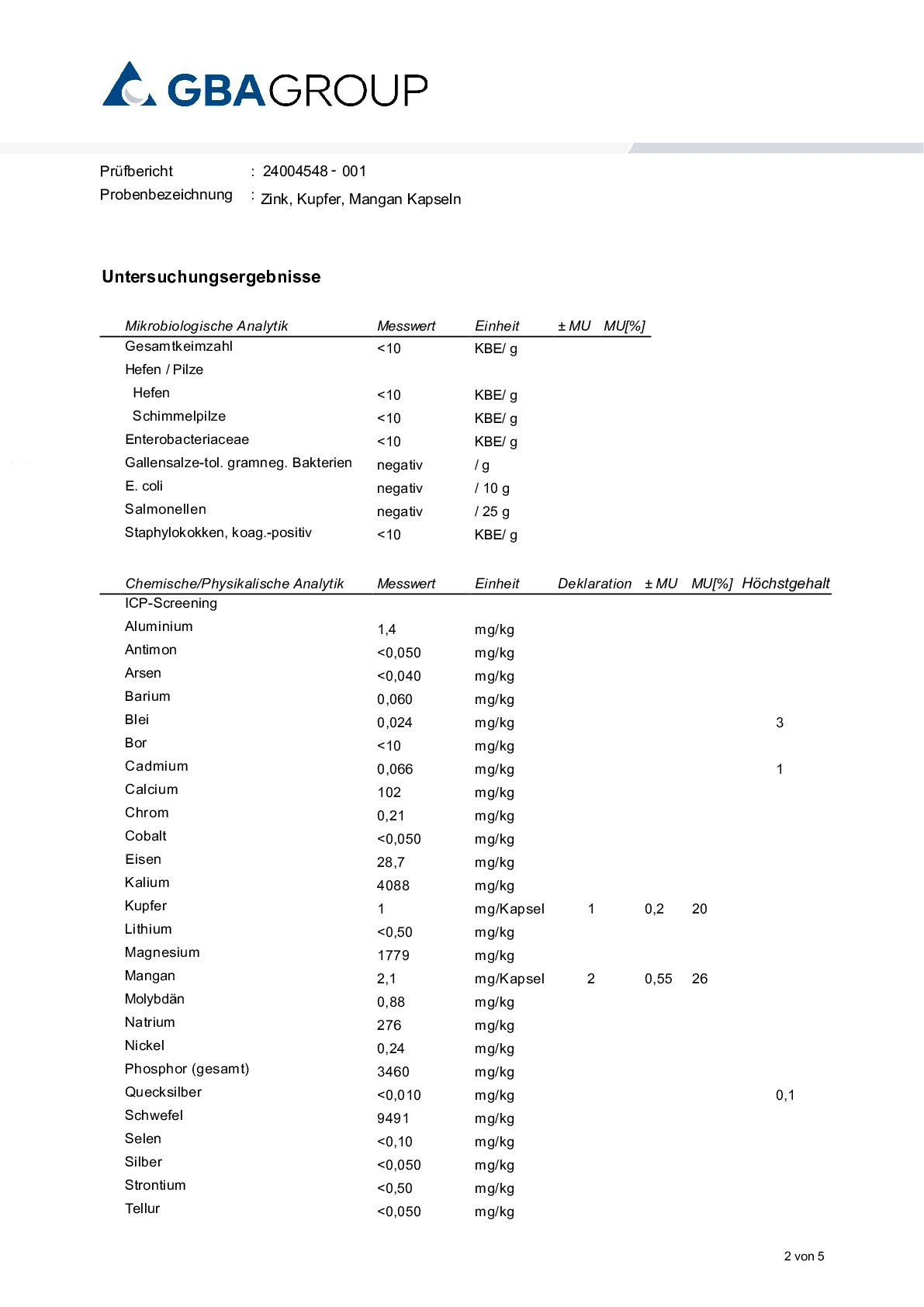
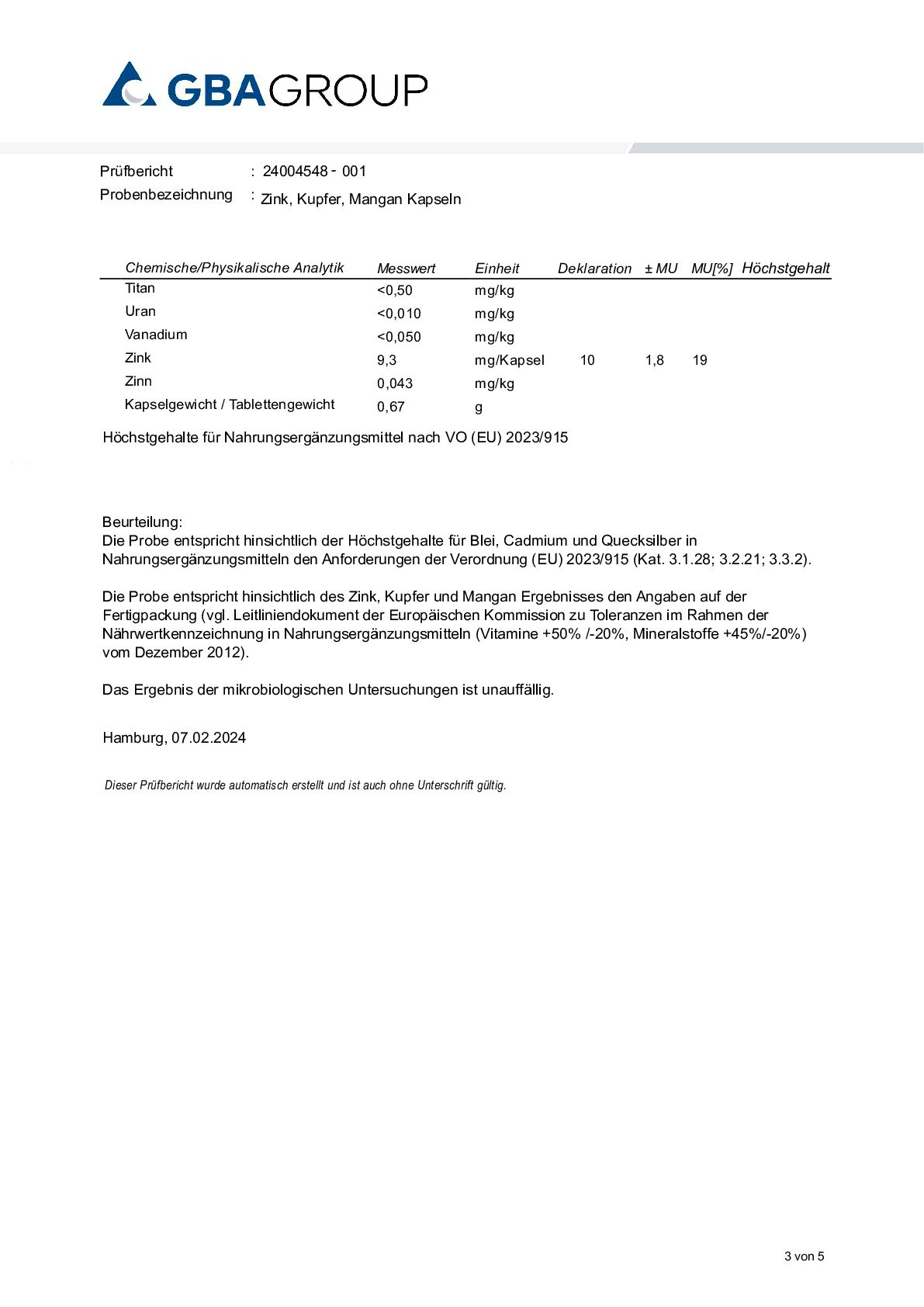
Zinc, Copper and Manganese
Zinc, copper, and manganese are essential trace elements that play a role in various enzymatic and antioxidative repair processes in the body.
Zinc is not only important for the immune system, but also serves to maintain healthy skin, hair, nails, and bones, as well as testosterone levels and vision. Zinc is also important for the synthesis and breakdown of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins.
Copper plays an important role in the maintenance of connective tissue as well as in the production of pigmentation for skin, hair, and red blood cells. Copper is indispensable for iron intake as well as the formation of various tissues including nerve fibres. Copper promotes wound healing and contributes to healthy immune defence.
Manganese is a component of many enzymes, protects DNA, proteins, and lipids against oxidative stress, and contributes to the maintenance of bones and energy metabolism.
Zinc
Zinc is a vital essential trace element, and part of more than 300 important enzymes. It influences more than 3,000 bodily proteins, and plays a role in numerous important processes. Zinc is necessary for maintaining the immune system, metabolism and fertility. It is also necessary for cell division and DNA synthesis as well as healthy vision and hair and nail growth.
Health Benefits of Zinc According to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)
Zinc contributes to:
- The protection of cells from oxidative stress
- Normal cognitive function
- The normal function of the immune system
- Normal acid-base metabolism
- Normal carbohydrate metabolism
- Normal metabolism of fatty acids
- Normal DNA synthesis
- Normal fertility and reproduction
- Normal macronutrient metabolism
- Normal metabolism of vitamin A
- Normal protein synthesis
- The maintenance of normal bones, nails, skin and hair
- The maintenance of normal vision
- The maintenance of normal testosterone levels in the blood
and zinc has a role in the process of cell division.
Copper
Copper is a component of a range of enzymes and many redox reactions. The main function of this trace element is its contribution to haematopoiesis, energy metabolism, and antioxidative defence.
Health Benefits of Copper According to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)
Copper contributes to:
- The protection of cells from oxidative stress
- The normal function of the immune system
- Maintenance of normal connective tissues
- Normal energy-yielding metabolism
- Normal functioning of the nervous system
- Normal hair and skin pigmentation
- Normal iron transport
Manganese
The trace element manganese contributes to a variety of metabolic processes within the body. Manganese is a component of many enzymes, protects DNA, proteins, and lipids against oxidative stress, and contributes to the maintenance of bones and energy metabolism. As a part of the enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD), manganese plays a special role in protecting cells: proteins, lipids, and DNA can thus be protected against oxidative stress. Not least, manganese also contributes to healthy bone structure and normal connective tissue formation. Manganese gluconate is an organic form of manganese and is quite bioavailable. Along with zinc, iron and copper, manganese is an essential trace element that must be supplied daily in sufficient quantities and is not only a component of vital enzymes, but also activates them at the same time.
Health Benefits of Manganese According to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)
Manganese contributes to:
- The protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage
- The maintenance of normal bones
- The maintenance of normal energy metabolism