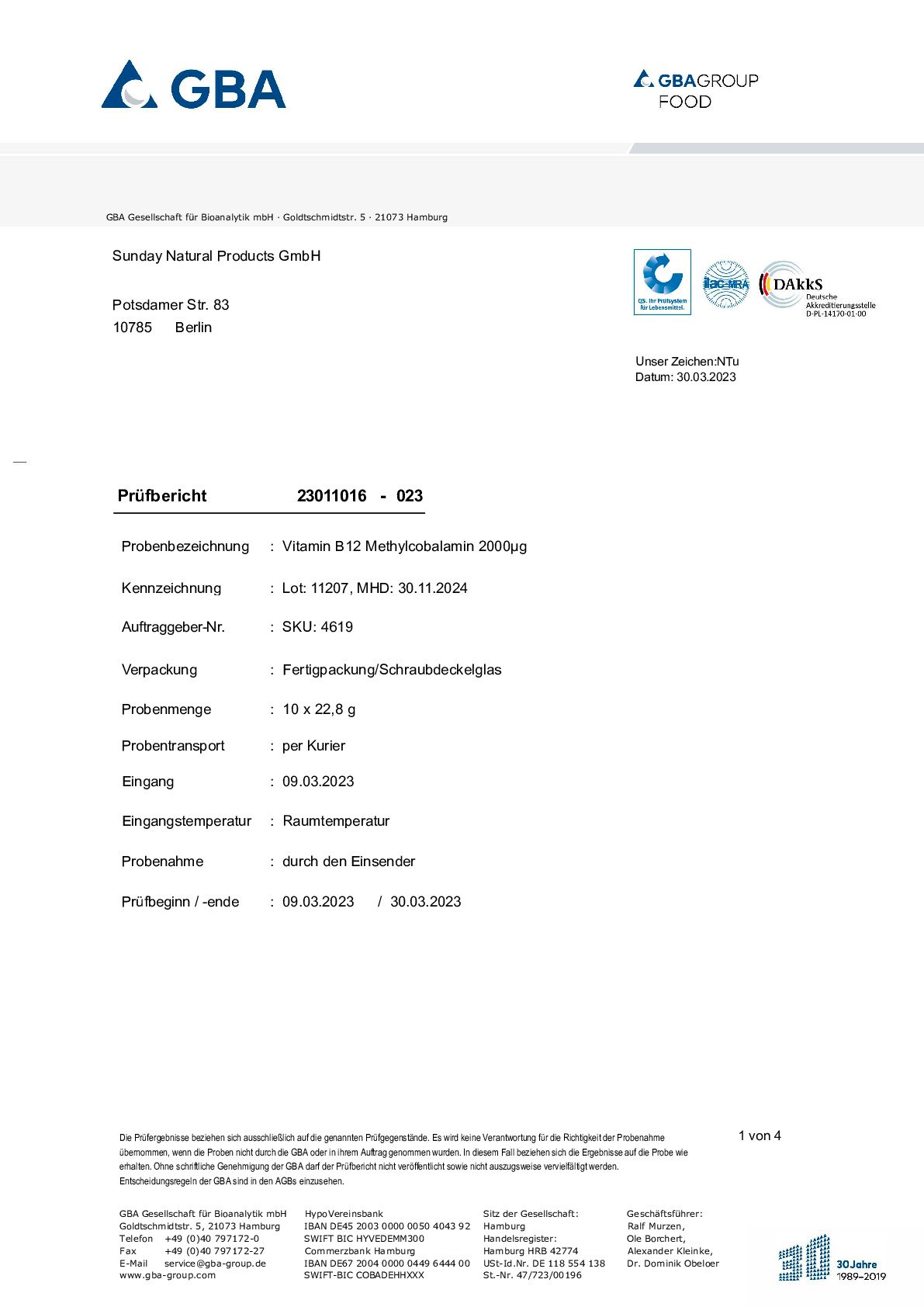
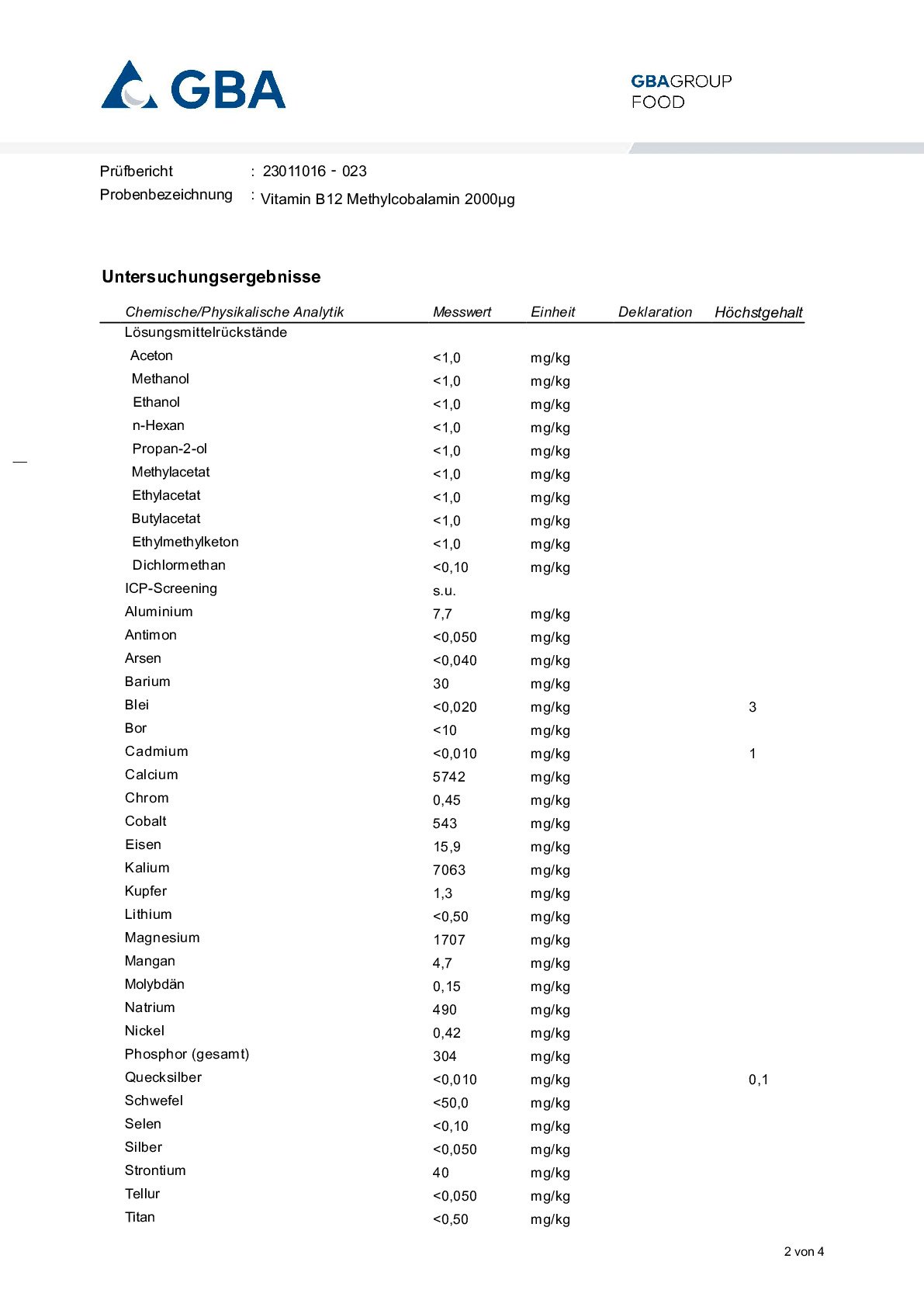
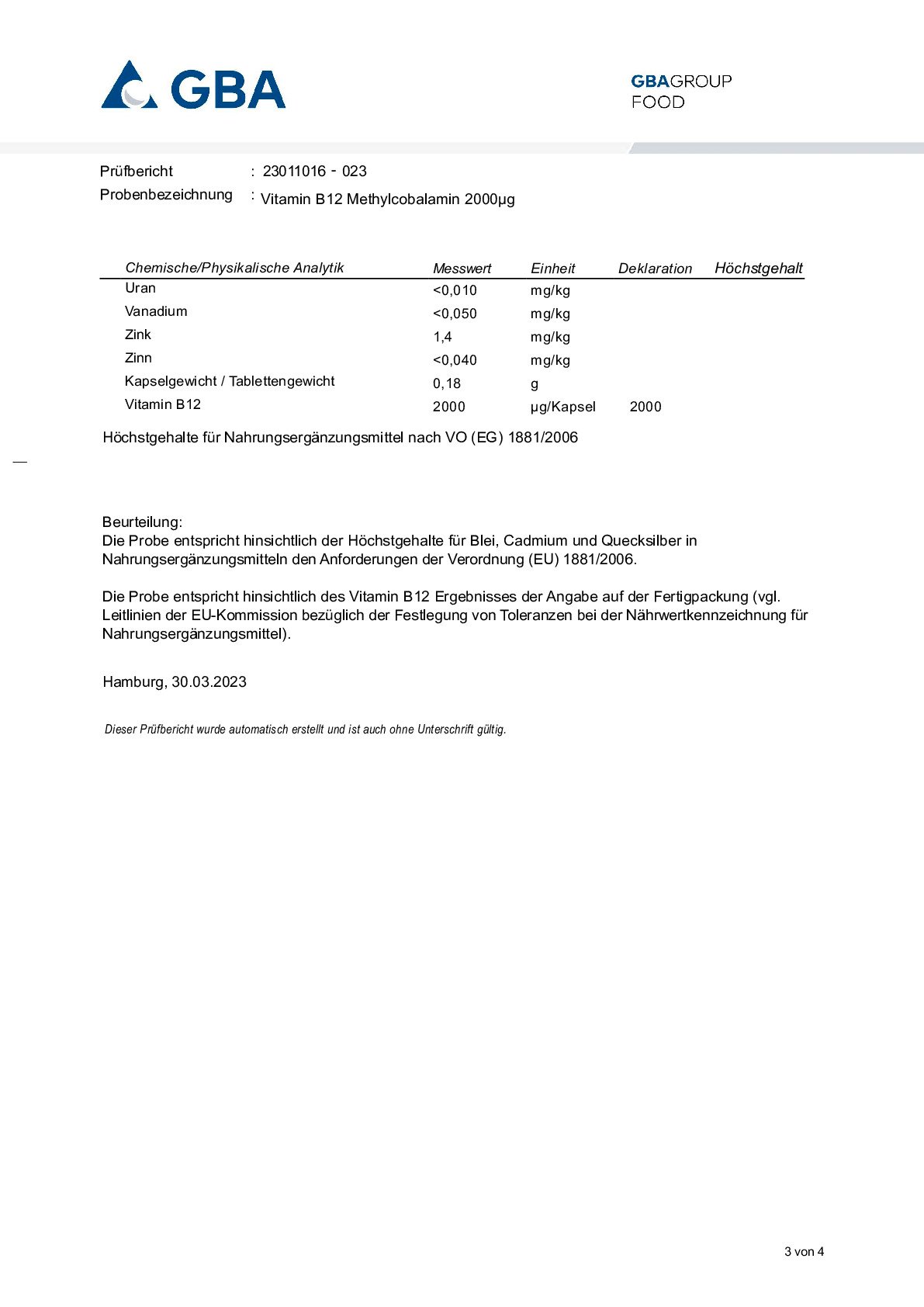
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Vitamin B12 fulfils a number of important functions in the body. Among other things, it can help to reduce tiredness and fatigue and maintain a normal energy metabolism. It contributes to the normal functioning of the psyche, immune and nervous systems, supports the formation of red blood cells and is beneficial for normal homocysteine metabolism. The body also needs vitamin B12 for cell division. Vitamin B12 acts as a so-called coenzyme in the body, meaning it is necessary for certain enzymes in our body to fulfil their tasks. The associated reactions are directly dependent on vitamin B12 and cannot take place without the vitamin.
Natural and Bioactive Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 exists in different chemical forms, each with different functions within the body. The natural forms of vitamin B12 that can be readily absorbed by the body are described as "bioactive coenzymes". Synthetic forms of Vitamin B12 such as cyanocobalamin must be first converted into a natural form by the body in order to be effective, which is why we use naturally bioactive forms of Vitamin B12 that the body can directly use.
Methylcobalamin
Methylcobalamin is one of the two so-called bioactive coenzyme forms of vitamin B12. It is highly bioavailable and can be directly utilised by the body without prior conversion.
Methylcobalamin is the predominant form of vitamin B12 in the bloodstream and cytoplasm. Along with folate, this coenzyme plays an integral role in the methylation cycle, which is important in many bodily processes including cell division and hormone and neurotransmitter synthesis. Methylcobalamin is responsible in these reactions for the breakdown of harmful homocysteine. This coenzyme has also been shown to positively contribute to a sense of well-being as well as the regeneration of nerves.
Health Benefits of Vitamin B12 According to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA):
Vitamin B12 contributes to:
- Normal energy-yielding metabolism
- Normal functioning of the nervous system
- Normal homocysteine metabolism
- Normal psychological function
- Normal red blood cell formation
- The normal function of the immune system
- The reduction of tiredness and fatigue
- Vitamin B12 has a role in the process of cell division