Chromium is an essential trace element and contributes to the metabolism of macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, fat) and to the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels.
Chromium plays a role in the formation of the glucose tolerance factor (GTF), which increases insulin sensitivity and thereby influences blood glucose levels. A chromium deficiency can therefore lead to reduced glucose tolerance with fluctuating blood glucose levels and, in the long term, to elevated blood glucose levels.
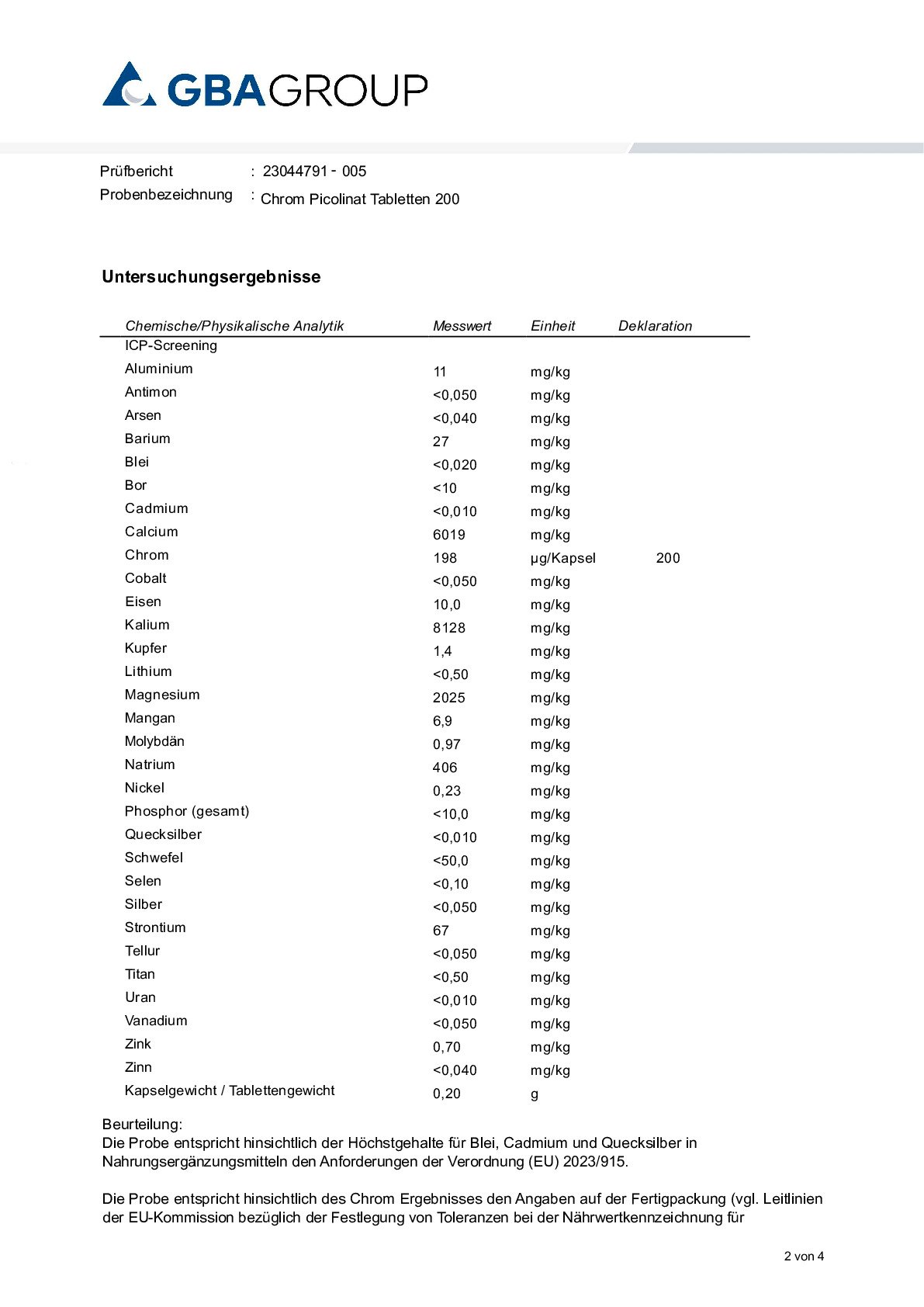
Chromium picolinate has significantly better bioavailability compared to other chromium compounds such as chromium chloride.
According to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA):
Chromium contributes to:
- Normal macronutrient metabolism
- The maintenance of normal blood glucose levels